

Pharmacological classification
Medicines acting on the gastrointestinal tract – Other Omeprazole is an inhibitor of the gastric proton pump (H+, K+-ATPase). It inhibits both basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion by parietal cells, whether induced by acetylcholine, gastrin, or histamine.
Omeprazole does not affect acetylcholine, histamine, or gastrin receptors.
Mechanism of action
Omeprazole is an inhibitor of the gastric proton pump (H+, K+-ATPase). It inhibits both basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion by parietal cells, whether induced by acetylcholine, gastrin, or histamine.
Omeprazole does not affect acetylcholine, histamine, or gastrin receptors.
Strengths
10 mg capsule, 20 mg capsule, 40 mg capsule
Pack size
OMEZ 10 white HDPE bottles containing 30 capsules.
OMEZ 20 white HDPE bottles containing 30 capsules.
OMEZ 40 white HDPE bottles containing 30 capsules.
Indications
Adults:
Duodenal ulcer, including prevention of relapse
Gastric ulcer, and reflux oesophagitis
Long-term management of reflux oesophagitis and Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Symptomatic relief of heartburn in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and the short-term relief of functional dyspepsia
Helicobacter pylori-positive duodenal ulcers as part of an eradication program with appropriate antibiotics
Treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs -associated gastric and/or duodenal ulcer/erosions
Reduction of the risk of developing gastric and/or duodenal ulcer/erosions
Reduction of the risk of relapse for previously healed gastric and/or duodenal ulcer/erosions in patients on NSAID treatment.
Children:
Short-term (up to 3 months) treatment of severe ulcerative reflux oesophagitis resistant to previous medical treatment.
Dosage
Duodenal ulcer
20 mg once daily for two to four weeks. In some duodenal ulcer patient's refractory to other treatment regimens, 40 mg once daily may be effective.
Prevention of relapse in patients with duodenal ulcer
10 mg once daily. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 20 to 40 mg once daily. The above-recommended dosage regimens are inclusive of Helicobacter pylori-positive duodenal ulcers as part of the eradication programme with appropriate antibiotics.
Gastric ulcer and reflux oesophagitis
20 mg once daily for four to eight weeks. In some gastric ulcer and reflux oesophagitis patient's refractory to other treatment regimens, 40 mg once daily may be effective. For the long-term management of patients with reflux oesophagitis the recommended dose is 20 mg once daily. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 20 to 40 mg once daily. In patients with severe or symptomatic recurrent reflux oesophagitis treatment can be continued with OMEZ at a dosage of 20 mg once daily.
NSAID-associated gastro-duodenal lesions with or without continued NSAID treatment
20 mg once daily. In most patients, healing occurs within 4 weeks. For patients who may not be fully healed after the initial course healing usually occurs during a further 4 weeks of treatment.
Prevention of NSAID-associated gastro-duodenal lesions and dyspeptic symptoms
20 mg once daily.
Symptomatic gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
20 mg daily. Patients may respond adequately to 10 mg daily; therefore, individual dose adjustments should be considered. If symptom control has not been achieved after four weeks of treatment with the prescribed daily dose further investigation is recommended.
Dosage
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
60 mg once daily. The dosage should be adjusted individually, and treatment continued as long as it is clinically indicated. With doses above 80 mg daily, the dose should be divided and given twice daily. There is very limited experience with the use of OMEZ in children.
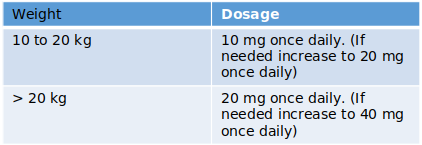
Severe ulcerative reflux oesophagitis in children from one year and older
Recommended dosages:
*For further information on contra-indications, side-effects, special warning, and storage instructions, please refer to the professional information by clicking below.